|
Measuring the air speed of model aircraft with pitot tube
The pitot tube in question consists of two coaxial tubes. The inner tube opens up to the tip of the instrument and measures the total pressure generated by the airflow. The outer tube has small holes for static pressure measurement.
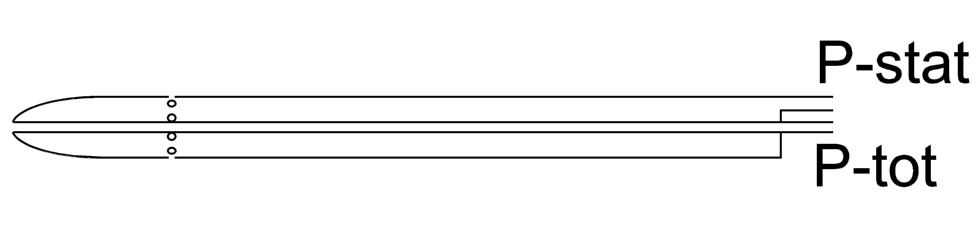
The speed of the airflow can be calculated with following formula:
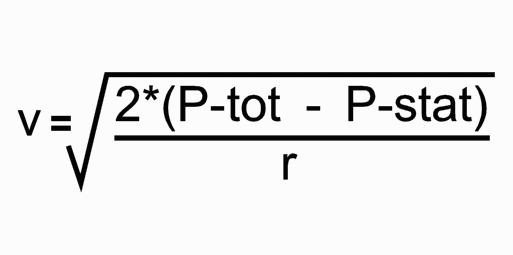
v = speed of airflow [m/s]
P-tot = total pressure [Pa]
P-stat = static pressure [Pa]
r = density of the gas measured [kg/m3]
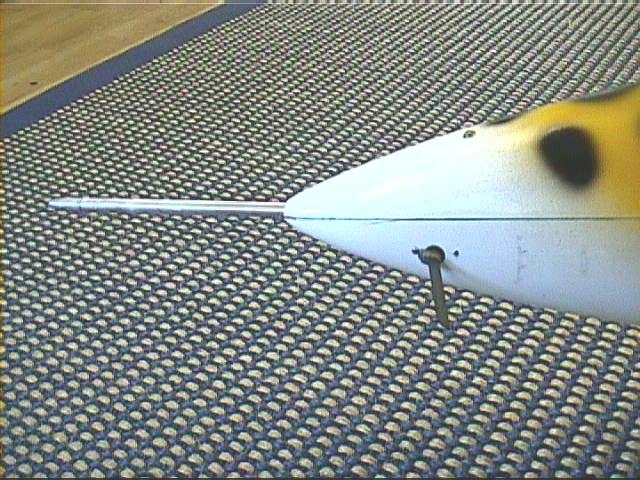

In model aircraft use, the pitot tube is recommended to be removable, so that it will not be damaged in transportation.
Another good possibility is to use the nose of the plane as an pitot tube. In this case you just have to find a correct spot for the static measurement holes from the sides of the fuselage.
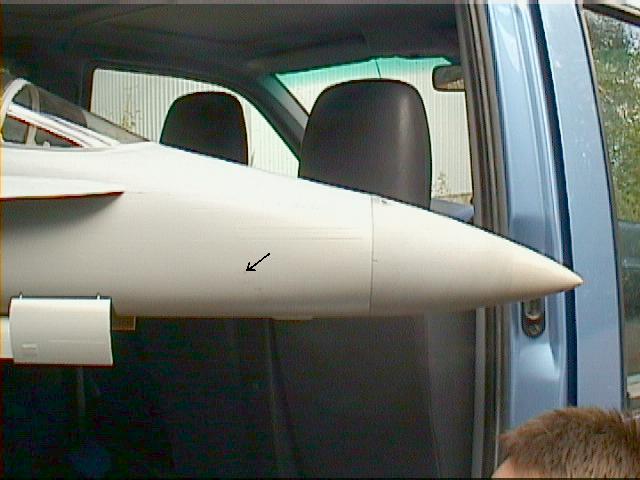

In this example, the static measurement holes for this Real Design F-18C Hornet are small needle holes in either side of the front fuse, connected together and then lead to the FDR static pressure sensor. The small arrow indicates the hole position.
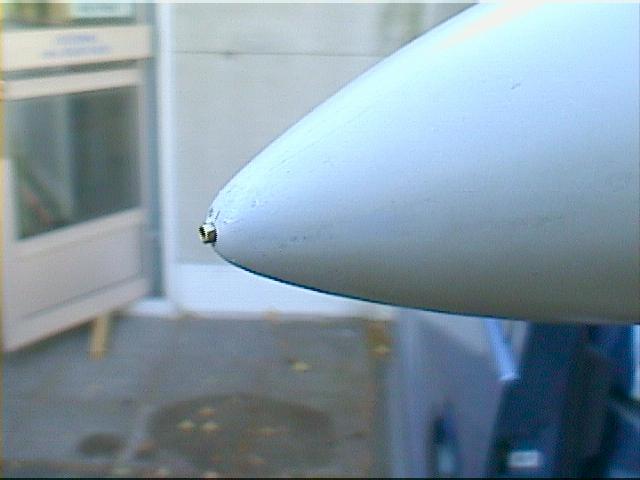

The total pressure is measured with the tube sticking out from the tip of the nose cone.
|